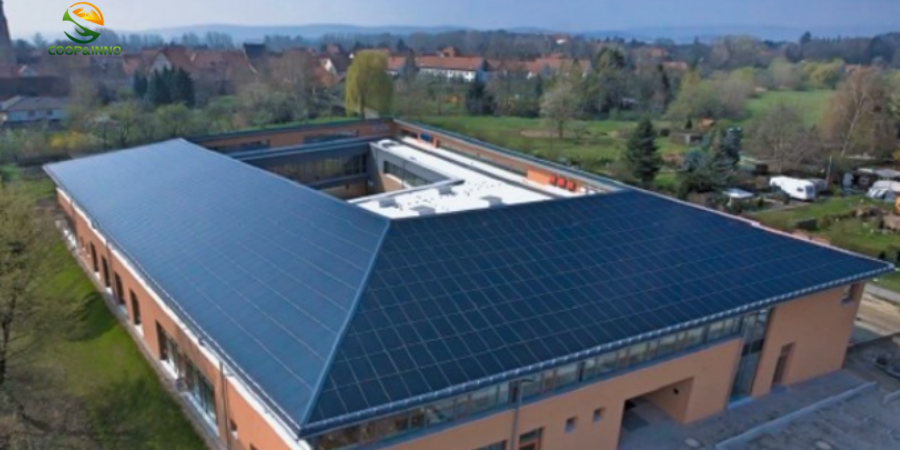
Building photovoltaics: BAPV and BIPV
Hello everyone, today I will talk to you about BIPV. Before talking about BIPV, let's take a look at the position of BIPV in photovoltaic power stations. Building photovoltaics belong to distributed photovoltaics. Compared with centralized photovoltaic power stations, they have the advantages of saving land, local consumption, and power peak regulation. Building photovoltaics is to combine photovoltaic power generation with buildings, and lay photovoltaic devices on the periphery of the building structure to generate electricity.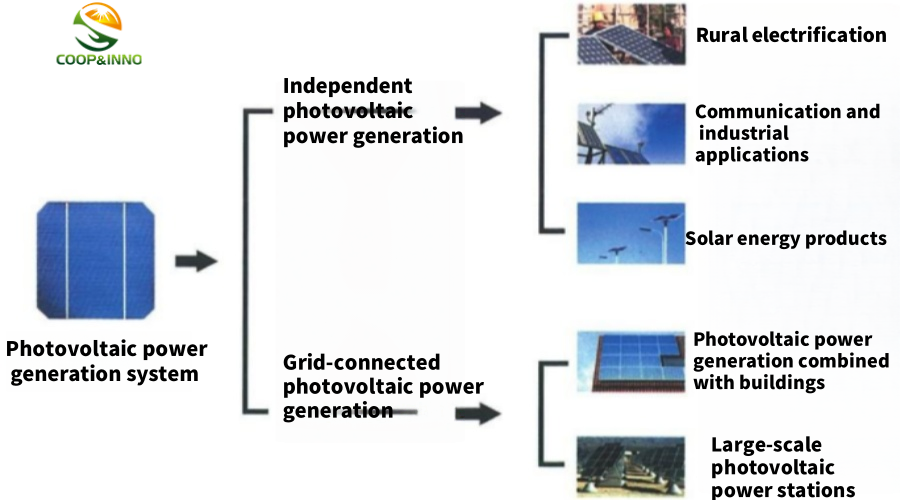
Classification of photovoltaic power stations
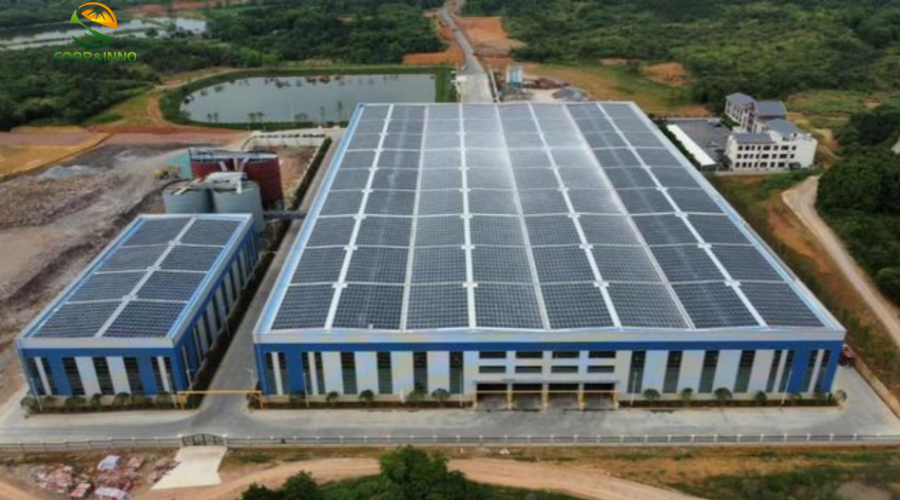
And photovoltaics combined with buildings are divided into two categories:1. BAPV, installed photovoltaics, Building attached photovoltaics, photovoltaic systems attached to the surface of the building.2. BIPV, Building integrated photovoltaics, Building integrated Photovoltaic, photovoltaic systems become direct building materials.BAPV is a simple combination method, suitable for the renovation of existing roofs. Directly install additional steel structure brackets or slide rails on the roof of the building, and fix photovoltaic panels to generate electricity. At present, the photovoltaic roofs that are "promoted throughout the county" all adopt this method.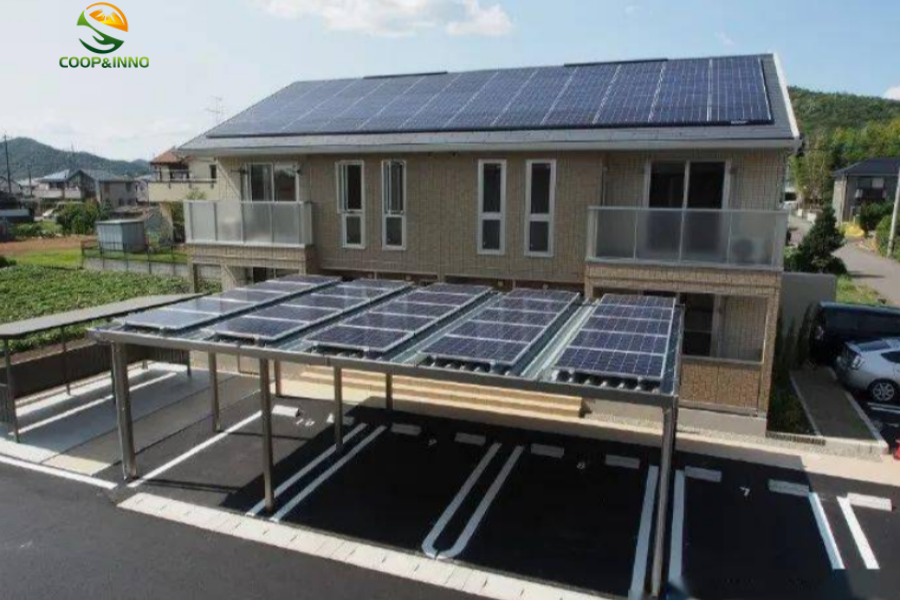
Typical application of BAPV
The main problems encountered by BAPV are!1. Load. The original roof load does not meet the requirements of secondary installation of photovoltaic panels, and the original roof needs to be reinforced. Some reinforcements are difficult. There are even news reports of snowstorms collapsing roofs and strong winds blowing away photovoltaic panels.2. Waterproofing. BAPV will damage the original roof waterproofing layer, and it needs to be repaired after construction, which will bring drainage hazards.3. Safety and actual service life of photovoltaic panels. Ancillary components such as inverters and junction boxes are often exposed to the outside, affecting the appearance and being easily damaged, reducing the actual service life of BAPV:BAPV is often a project that requires a one-time investment for many years of return, and the owner attaches importance to yield and safety. Once a major loss occurs, it will be difficult to effectively protect the rights and interests. BIPV, photovoltaic and building integration, can avoid many problems of BAPV. It has the advantages of long life, reliable force, reliable waterproofing, and convenient operation and maintenance.BIPV classification and developmentBIPV is a photovoltaic system that becomes a direct building material. Currently, a series of photovoltaic building materials such as photovoltaic roofs, photovoltaic glass, photovoltaic curtain walls, and photovoltaic tiles have been developed.
Comparison of BIPV related products with BAPV
BIPV can be divided into crystalline silicon type and thin film type according to materialsCrystalline silicon BIPV has high conversion efficiency, and single crystal can reach 25%. Crystalline silicon cells are opaque, and crystal modules are mainly used in opaque building projects. Of course, the use of double-sided glass in crystalline silicon photovoltaic curtain walls can also meet certain light transmission requirements. Crystalline silicon type is the most familiar to everyone.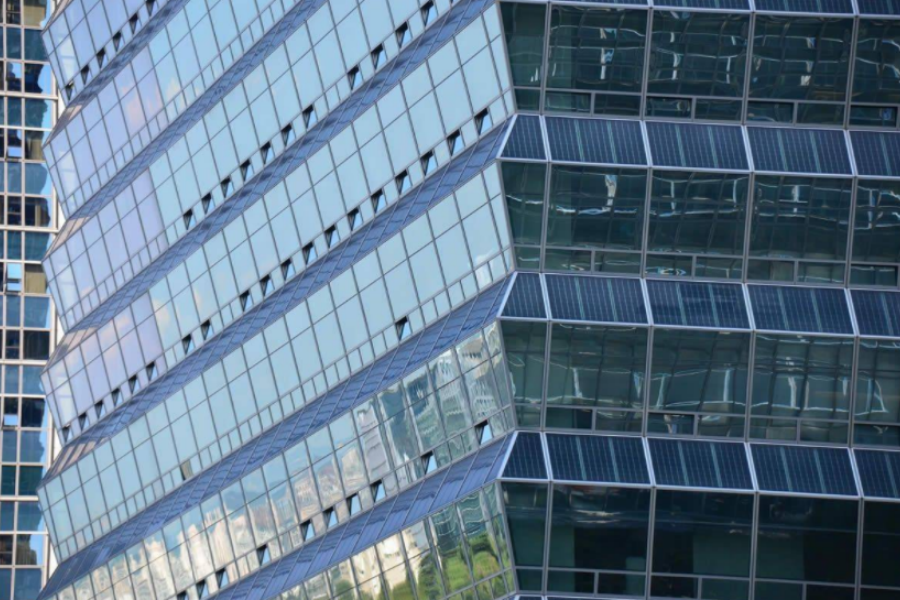 Thin film BIPV, currently mainly cadmium telluride (CdTe) cells, copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) cells, and perovskite solar cells.The average efficiency of cadmium telluride in commercial applications is 14.7%. Copper indium gallium selenide cells are currently the most efficient among thin film types, which can be close to 20%. The efficiency is not as good as that of crystalline silicon, but the thin-film type also has advantages that the silicon type does not have: adjustable transparency, better low-light performance, and better temperature coefficient. It ensures that it can maintain operation under extreme conditions such as high temperature and low light.
Thin film BIPV, currently mainly cadmium telluride (CdTe) cells, copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) cells, and perovskite solar cells.The average efficiency of cadmium telluride in commercial applications is 14.7%. Copper indium gallium selenide cells are currently the most efficient among thin film types, which can be close to 20%. The efficiency is not as good as that of crystalline silicon, but the thin-film type also has advantages that the silicon type does not have: adjustable transparency, better low-light performance, and better temperature coefficient. It ensures that it can maintain operation under extreme conditions such as high temperature and low light.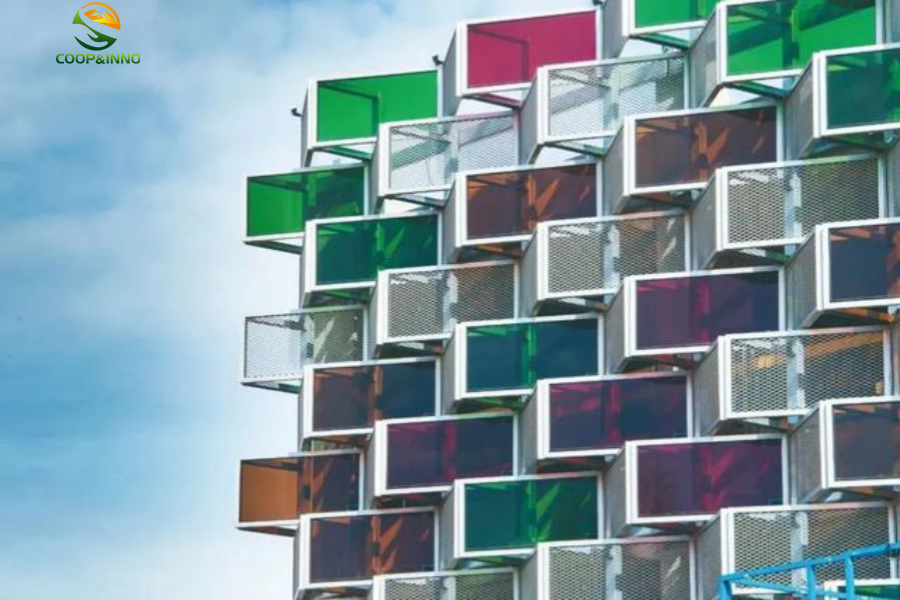
Architectural effect of colored thin-film batteries
Thin-film batteries are not a new concept that has only recently emerged. Thin-film battery technology was introduced in the 1970s, and it was more popular than crystalline silicon batteries and was even called the "next generation of photovoltaic technology." Later, due to the difficulty in improving efficiency, it gradually died down.Nowadays, the outbreak of BIPV has brought new opportunities to film batteries. At present, domestic companies in the field of BIPV include Longyan Energy, Mingyang Smart Energy's subsidiary Ruike New Energy, Hangzhou Xianna, etc. However, crystalline silicon batteries have major giants in the photovoltaic industry (Longi, Trina, Jinko, JA Solar, Lianbang, Canadian Solar, etc.). At present, the crystalline silicon camp looks more gorgeous.BIPV can be divided into building material type and component type according to product form"Building material type" is more integrated, and photovoltaic cells are fully integrated into building materials. From the appearance, it may not be much different from traditional building materials. It puts forward higher requirements on material strength and performance. "Building material type" is a relatively ideal form, but it has a high degree of customization, high strength requirements, and high cost."Component type" tends to be standardized products, combining photovoltaic components with building components into integral components, which are easier to distinguish from traditional building materials in appearance. This is the mainstream in the market at present, mainly photovoltaic roofs, photovoltaic walls, and photovoltaic sunshades. On the one hand, it can maintain the power generation efficiency of components to the highest extent and maximize the effective power generation area of batteries. However, standardized components also limit the application scenarios. At present, they are mainly used in the outer curtain walls of large buildings with large roofs such as industrial and commercial factory roofs and rainproof carports.Now photovoltaic component companies have also launched translucent and colorful photovoltaic curtain walls, providing design institutes with more optional design styles to meet certain architectural aesthetic design requirements. Photovoltaic curtain walls have both photovoltaic and architectural attributes. They must be designed, constructed and installed at the same time as the building, and the cost is relatively high. In addition to the power generation function, it must meet the architectural function requirements: external maintenance, transparency, mechanics, aesthetics, safety, etc. The architectural function requirements are higher than the photovoltaic power generation requirements, and the architectural function requirements must be met first, so sometimes the photovoltaic properties are sacrificed, such as higher power generation efficiency, better light angle, larger power generation, etc.








